서울시에서 지하안전 확보를 위한제도와 운영시스템은 무엇인가요?

박 민 철
서울연구원 인프라기술연구실
연구위원
(mcpark@si.re.kr)
서울시는「지하안전관리에 관한 특별법」에 근거하여 지반침하 예방과 지하안전 확보를 위한 제도적·기술적 관리체계를 단계적으로 구축해 왔습니다. 본 답변에서는 서울시 지하안전관리의 제도적 기반과 운영 시스템의 소개와 발전 방향을 독자분들게 소개해드리고자 합니다.
서울시는 지반침하로 인한 위해를 방지하고 공공의 안전을 확보하기 위해 제정된「지하안전관리에 관한특별법」제7조 1항에 따라 지하안전관리에 관한 계획을 수립하고 있습니다. 추진 목적으로는 지반침하 예방및 안전관리를 지자체 중심으로 실효성을 제고하고, 지반침하의 근본적인 원인 해소 및 사전 예방 활동을 강화하고, 신기술 도입 등 다각적인 정책 추진으로 통해 시민 불안감을 해소하자 합니다.
2025년도 서울시 지하안전관리 계획은 ① 노후 지하시설물 집중정비 추진, ② 지반침하 예방활동 확대 및강화, ③ 스마트 지하안전관리 기술 도입, ④ 지하안전기관 협력체계 구축의 4개 추진 전략으로 세부 10개 세부과제로 구성되어 있습니다.
첫 번째로 노후 관로의 증가로 예측·예방 중심의 관리 패러다임을 전환하고 지하 안전관리 기술 고도화를기본 방향으로 상수관로의 선제적 누수탐사와 지반침하 취약시설물의 순찰·점검 강화, 노후 하수도 정비를확대 추진하고 있습니다.
두 번째로 지반침하 예방활동은 공동조사(GPR탐사) 강화, 예방 순찰활동 강화, 굴착공사장 안전점검 추진,지반침하 중점관리대상 관리 강화, 지하안전평가 대상 사업 공사장 계측관리의 세부과제로 구성됩니다. 공동조사(GPR탐사)는 그림 1과 같이, 1차 탐사로 차량형 멀티GPR로 탐사 자료를 취득하고 공동 신호 분석으로공동으로 의심되는 신호 위치(POI, Point of Interest)를 파악한 후 공동 확인을 위한 2차 조사로 핸드 GPR탐사와 천공 및 영상촬영으로 공동 유무와 규모를 파악하고 있습니다. 올해부터는 연구사업을 통해 인공지능을이용하여 공동 신호 분석에 대한 정확도와 오탐율을 개선하고 있습니다.
세 번째로 스마트 지하안전관리 기술 도입은 우선정비구역도 구축 활용, 지반침하 관측망 설치, 공동조사(GPR탐사) 장비 성능 검증 강화입니다. 지역별 지반침하 가능성을 평가하고 지하매설물 등 시설물 우선 정비의 필요성을 등급화하여 도면화한 우선정비구역도를 활용하여 GPR탐사 강화 및 위험 시설물 우선 정비를추진하고, 효율적 안전대책 수립을 위해 관련 부서에 우선정비구역도 정보를 제공하고 있습니다. 또한, 지반내 관측센서를 설치하여 지반 변동량을 실시간으로 측정, 잠재적 위험을 사전에 인지하여 선제적으로 대처하기 위한 지반침하 관측망을 대규모·대심도 굴착공사장 및 지하수 유출량이 많은 지역 주변에 설치하고 운영시스템을 구축하였습니다.


올 9월부터는 그림 2와 같이, ‘지반침하 신속현장점검시스템’을 도입하였습니다. 지반침하 발생시 지하안전자문단 파견, GPR탐사 등으로 2차 사고 예방, 원인조사 및 재발방지를 강화한 지반침하 대응시스템을 구축운영하고 있습니다. 토질 및 기초, 상하수도 등 지하안전 관련 전문가로 구성된 ‘지하안전자문단’을 운영하여, 침하 원인조사 및 재발방재 대책 수립에 공학적 자문을 수행하고 있습니다. 지하안전전문가 확충을 위해서울시는 우리학회, 대한토목학회, 한국터널지하공간학회와의 협약을 통해 자문단을 확대하고 사고 조사·현장 대응 역량을 강화하였습니다.
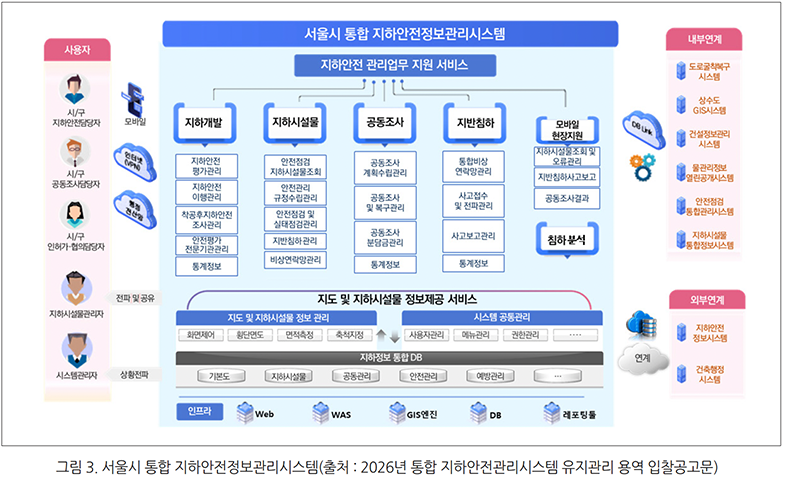
서울시는 그림 3과 같이 통합 지하안전정보관리시스템도 최적 운영, 시스템 활용성 유지, 행정 평의성 제공, 서비스 안정화 확립을 위해 지속적으로 유지관리 하고 있습니다. ‘서울시 통합 지하안전정보관리시스템’은 지하안전 관리 업무 지원 서비스로 지하개발, 지하시설물, 공동조사, 지반침하, 모바일 현장지원, 침하 분석까지의 기능을 지하안전 담당자, 공동조사 담당자, 시/구 인허가·협의담당자, 지하시설물 관리자 등의 사용자에게 제공하며, 내/외부 관련시스템과의 연계를 통해 최적의 정보제공 서비스를 운영하고 있습니다.
마지막으로 지하안전 기관 협력체계 구축은 지자체 업무 관계자 및 지하시설물 관리자 정보를 통합 지하시설물 시스템에 등록 및 상시 공유하여 통합 지하안전시스템을 활성화하기 위한 목적으로, 지반침하 사고발생시 직시 통보 및 시스템 입력 및 신속한 공동복구 협업을 추진하고 있습니다. 그리고 그림 3의 통합 지하안전관리시스템 이용 활성화를 추진하고, 정기 지하시설물 현황조사와 지반침하 매뉴얼 정비 및 지하안전업무교육을 연계하여 추진 중에 있습니다.
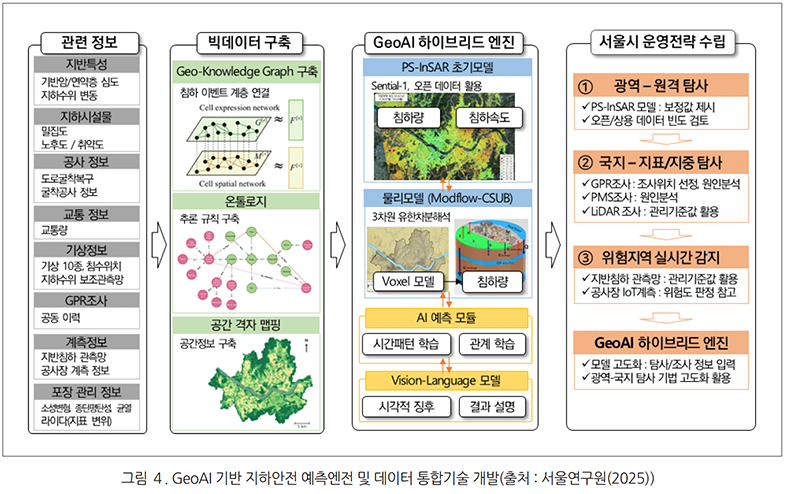
서울연구원에서는 서울시의 지하안전 관련 정책과 기술 지원을 위해 서울특별시 지반특성분석지도 모델개발을 수행 중에 있고, 지반침하 사고 예방을 위한 첨단기술 활용성 검토 등의 과제를 수행 중에 있습니다.내년에는 GeoAI 기반 지하안전 예측엔진 및 데이터 통합기술 개발(그림 4 참고)과 지반침하 사고 예방을 위한 도로굴착복구 공사의 되메우기 품질향상 방안, GPR공동조사 결과 분석과 이에 대응하는 발생원인별 대응방안 마련을 위한 연구과제도 추진하고자 합니다
참고문헌
1. 서울특별시(2025), 서울특별시 2025년 지하안전관리계획
2. 서울시 안전소식(2025), “서울특별시 지하안전을 책임집니다”, https://news.seoul.go.kr/safe/archives/516869
3. 서울시 보도자료, https://mediahub.seoul.go.kr/archives/2012160
4. 서울연구원(2025), “GeoAI 기반 지하안전 예측엔진 및 데이터 통합 기술 개발” 연구사업계획서
국제학술회의 소식
International Conference & Symposium
대륙별 학회 (Date : Day-Month-Year)
참고 웹사이트 : https://www.issmge.org/events
2026
아메리카(북·남미)
International Symposium on Tailings Deposits
o Date: March 11-13, 2026
o Venue: Mexico
o Website: https://2sisdj-hermosillo-2026.com.mx/
o E-mail: manicam@smig.org.mx
유럽
2nd International Scientific and Practical Conference on Soil Mechanics, Geotechnics
and Foundation Engineering. Intelligence on Guard of Mechanical Safety - GEOMOS26
o Date: March 17-20, 2026
o Venue: Moscow, Russia
o Website: https://geomos.rssmgfe.ru/en/
o E-mail: geomos@niiosp.ru
15th International Conference "Modern Building Materials, Structures and Techniques"
o Date: May 12-15, 2026
o Venue: Vilnius, Lithuania
o Website: https://www.rilem.net/agenda/15th-international-conference-modernbuilding-materials-structures-and-techniques-1650
o E-mail: mbmst@vilniustech.lt
8th International Young Geotechnical Engineers Conference
o Date: June 11-14, 2026
o Venue: Graz, Austria
o Website: https://iygec2026.tugraz.at
o E-mail: iygec2026@tugraz.at
21st International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering
o Date: June 14-19, 2026
o Venue: Vienna, Austria
o Website: https://www.icsmge2026.org/en/
o E-mail: helmut.schweiger@tugraz.at
International Conference on Advances and Innovations in Soft Soil Engineering 2026
o Date: August 24-26, 2026
o Venue: Delft, Netherlands
o Website: TBA
o E-mail: s.muraro@tudelft.nl
CREST 2026
o Date: September 7-8, 2026
o Venue: Cambridge, United Kingdom
o Website: https://engage-events.ifm.eng.cam.ac.uk/IC-CREST2026
Fourth International Symposium on Geotechnical Engineering for the Preservation ofMonuments and Historic Sites
o Date: September 16-18, 2026
o Venue: Athens, Greece
o Website: https://tc301-athens.com
o E-mail: secretary@tc301-athens.com
6th International Conference on Information Technology in Geo-Engineering
o Date: October 13-16, 2026
o Venue: Graz, Austria
o Website: https://www.icitg2026.com/
o E-mail: georg.erharter@ngi.no
아시아
o Date: January 28-30, 2026
o Venue: Taguig, Philippines
o Website: https://pssmge.org/
o E-mail: seagc.agssea@2026@gmail.com
Pan Mediterranean Geotechnical Engineering Conference
o Date: March 25-28, 2026
o Venue: Beirut, Lebanon
o Website: http://pmgec-leb.com/
o E-mail: contact@pmgec-leb.com
8th International Conference on Geotechnics, Civil Engineering and Structures (CIGOS)
o Date: April 16-17, 2026
o Venue: Ho Chi Minh city, Vietnam
o Website: https://cigos2026.sciencesconf.org/
o E-mail: cigos@avseglobal.org
12th International Symposium on Field Monitoring in Geomechanics 2026
o Date: August 06-10, 2026
o Venue: Indore, India
o Website: https://isfmg2026.com/
o E-mail: convener@isfmg2026.com
International Conference on Geotechnical Engineering | ICGE-Colombo 2026
o Date: August 24-25, 2026
o Venue: Colombo, Sri Lanka
o Website: https://icgecolombo2026.org/
o E-mail: slgssecretariat@gmail.com
2nd International Conference on In-Situ Measurement of Soil Properties and Case Histories (INSITU 2026)
o Date: September 21-23, 2026
o Venue: Bali, Indonesia
o Website: http://www.insitu2026.com
o E-mail: insitu2026@gmail.com
The 6th International Conference on Geotechnics for Sustainable Infrastructure Development
o Date: November 26-27, 2026
o Venue: Hanoi, Vietnam
o Website: https://geotechn.vn/
o E-mail: secretariat@geotechn.vn
오세아니아
Landslide Geo-Education and Risk(LaGER) 2026 - JTC1 & JTC3 workshop
o Date: April 28-May 01, 2026
o Venue: Queenstown, New Zealand
o Website: http://landsliderisk.nz/
o E-mail: ross.roberts@gmail.com
아프리카
10th African Young Geotechnical Engineers Conference
o Date: April 26-29, 2026
o Venue: Lagos, Nigeria
o Website: https://nige.org.ng
o E-mail: nsegeotechdiv@yahoo.co.uk
2027
아메리카(북·남미)
CPT'27: International Symposium on Cone Penetration Testing
o Date: May 12-14, 2027
o Venue: Vancouver, Canada
o Website: http://www.cpt27.org
o E-mail: kelly.cabal@conetec.com
유럽
IS-GI Lyon 2027: International Symposium on Ground Improvement
o Date:April 12-14, 2027
o Venue: Lyon, France
o Website: https://www.menard-group.com/isgi-lyon2027
o E-mail: fanny.maucotel@menard-mail.com
XVIII DANUBE-EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
o Date: June 09-12, 2027
o Venue: Budapest, Hungary
o Website: http://www.18decge.hu
o E-mail: info@18decge.hu
11th European Conference on Numerical Methods in Geotechnical Engineering
o Date: September 21-24, 2027
o Venue: Graz, Austria
o Website: http://numge2027.tugraz.at
o E-mail: numge2027@tugraz.at
2027
유럽
19th European Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Istanbul, Türkiye
o Date: August 20-25, 2028
o Venue: Istanbul, Turkey
o Website: http://zmgm.org.tr
o E-mail:info@zmgm.org.tr
손수원
경일대학교 건축토목공학과 조교수
(swson@kiu.ac.kr)
해외매거진 소개
Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering
VolumVolume 151, Issue 12 (December 2025) / / hhttps://ascelibrary.org/toc/jggefk/151/12

목차
Technical Papers
Multidirectional Cyclic Shear Behavior of Gap-Graded Soils Considering Fines Loss due to Suffusion: A DEM Perspective
Ruiyan Chen, Zheng Hu, Kun Pan, Qixin Wu and Zhongxuan Yang
Role of Soil-Well Interaction in the Transverse Kinematic Response of a Downhole Seismometer to S Waves: A ViscoelasticSolution
Liming Qu, Georges Kouroussis, Changwei Yang, Xuanming Ding and Yu Peng
Reliability of Axial Design Methods for Open Steel Piles Driven in Chalk
Tingfa Liu, Ken Vinck, Richard J. Jardine, Stavroula Kontoe and Roisin M. Buckley
Strength-Stiffness-Suction Relations of Compacted Silt
Kang Chen, Rui Zhang and Huan Wang
Excess Pore Pressure Generation and Liquefaction of Gravelly Soil
Amalesh Jana and Armin W. Stuedlein
Stress Ratio-Controlled Hardening Rule in the NorSand Framework
Seyyed Kazem Razavi and Samuel Yniesta
Relative Ice Saturation and Unified Elastoplastic Modeling of Frozen Soils
Kai-Qi Li and Zhen-Yu Yin
Evolution and Prediction of the Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity of Municipal Solid Waste during Long-Term Biodegradation Experiments
Xinlei Sun, Xiaoqing Pi, Jie Hu, Liangtong Zhan and Xunchang Fei
A Priori Estimation of the Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity of Municipal Solid Waste Using Empirical and Machine Learning Methods
Xinlei Sun, Yuanyuan Luo, Xiaoqing Pi, Xunchang Fei, Bate Bate and Yuliang Guo
Predicting Large-Scale Landslide Initiation Based on the Local Field Factor of Safety: An Application to the Braies Catchment in Northern Italy
Riccardo Busti, Giuseppe Formetta and Ning Lu
Cosserat Elastoplastic Finite-Element Model Incorporating Structural Properties of Natural Soil and Case Study of the Saint-Alban Embankment
Wencheng Wei, Hongxiang Tang, Xiaoyu Song and Xiaolong Ye
Modification of Clay with Sodium and Potassium Chloride Brines: Insights from Laboratory-Sedimented Samples of High-Plasticity Clay
Emil Mejlhede Kinslev, Irene Rocchi and Varvara Zania
Integration of Field Monitoring and Numerical Modelling to Evaluate the Construction Performance of a Deep-Sea Quay Wall
Fengwen Lai, Kevin Duffy, Ken Gavin, Dechun Lu and Alfred Roubos
Characteristics of Permanent Strain Accumulation and Resilient Modulus of Unsaturated and Structured Soil under Repeated Loads
Bao-Lin Dai and Chao Zhou
Reconciliation of the Effective Stress Equation between Macroscopic and Microscopic Static Equilibria
Jianhong Jiang and Longtan Shao
Lateral Inertial Pile-Soil Interaction Using an Analytical Model
Asrat Worku and Mathewos Endeshaw
Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering
Volume 152, Issue 1 (January 2026) / https://ascelibrary.org/toc/jggefk/152/1

목차
Technical Papers
Soil Freezing Characteristic Surface for Partially Frozen Soils
Antai Dong, Xiong Zhang and Ming Xiao
Creep Deformation and Long-Term Strength of Ice-Rich Permafrost in Northern Alaska
Ziyi Wang, Ming Xiao, Matthew Bray, Dmitry Nicolsky and Xiaohang Ji
Skeleton Structure of Segregated Ice Lenses in Frozen Soil and Its Effects on the Mechanical Properties
Ningyu Yang, Daoju Ren, Hao Zheng, Zongqin Cao, Junling Si and Lei Quan
Quasi-Region-Specific Liquefaction Probability Prediction Based on a Liquefaction Database
Jiun-Shiang Wang, Jianye Ching and Yu-Jhang Tu
Three-Dimensional Geological Modeling with Multisource Data Fusion
Zening Zhao, Luyu Ju, Limin Zhang, Haifeng Zou, Jian He, Yunhong Lv, Te Xiao and Guojun Cai
Water Transfer in Granite Residual Soil: A Dual-Porosity SWCC Model in Stage-Divided Drying
Wenqing Chang, Peng Liu, Xin Kang and Renpeng Chen
Effects of Triaxial Sample Scaling on the Mechanical Behavior of Alluvial Gravels
Gilbert Girumugisha, Carlos Ovalle, Holger Reith and Hans Henning Stutz
A Machine Learning-Based Predictive Model for Liquefaction Ejecta Manifestation in Stratigraphically Variable Sites
Lianne Brito, Shideh Dashti, Abbie B. Liel and Brad P. Wham
Experimental Study of Enhanced Vacuum Preloading Using Electroosmosis and Airbag Pressure for Dredged Clays Improvement
Hongping Meng, Aifang Qin, Dean Sun, Yajun Wu and Lianghua Jiang
Experimental Study on the Shear Mechanical Properties of the Grout-Soil Interface Considering Grout Permeation
Jianyong Han, Pengpeng Ni, Yang Chen, Xiaoyu Bai, Tianliang Li, Qinghai Wang, Jianxin Wu and Shunqi Tao
Drained Cyclic Response of Horizontal Circular Plate Anchors in Sand
Rene Sumantri Kurniadi, Anamitra Roy, Conleth D. O´Loughlin, Shiao Huey Chow and Mark J. Cassidy
Impact of Suction and Swell-Induced Softening on Pile Behavior in an Unsaturated Expansive Clay
Sonu Kumar, Ashutosh Kumar, Tiago A. V. Gaspar and Ashraf S. Osman
Multilayered Capillary Barrier Systems: Analytical, Numerical, and Experimental Study
Riccardo Scarfone and Simon J. Wheeler
Mitigation of Lateral Spreading Effects on Bridge Piles Using Tire-Derived Aggregate
Axel A. Yarahuaman, Sara Walston, Jason Melara, Xiao Tan, Ahmed Elgamal and J. S. McCartney
Evaluation of Liquefaction Ejecta Potential from Case Histories and Insights from Nonlinear Dynamic Analyses
Riwaj Dhakal, Nikolaos Ntritsos and Misko Cubrinovski
Flowability and Strength of Flowable Filling Materials Made from Cement-Stabilized Sand and Soft Clay: Conflicting Effects of Sand Addition
Junde Qin, Pudur Nandagoplan Svetha, Xinlei Sun and Yaolin Yi
Evolution of the Small-Strain Shear Modulus in the Slip Zone Soil of Accumulated-Layer Landslides as Influenced by Gravel Content
Deshan Cui, Mingjie Dai, XinLi Hu, Qiong Chen, Xiaoyu Meng and Haoran Sun
Thermal Effects on the Stability of Geosynthetic Reinforced Soil Walls
Fei Zhang, Wenxin Ji, Yufeng Gao, Dov Leshchinsky and Farshid Vahedifard
Effect of High-Temperature History on the Swelling Characteristics and Chemical Composition of Kunigel-V1 Bentonite
Kunlin Ruan, Hideo Komine, Daichi Ito, Hailong Wang, Haruya Suzuki and Qingyuan Zhao
Depletion of Antioxidants in Tensioned HDPE Geomembranes Exposed to Synthetic MSW Leachate
Haiping Fu, Sana Ullah and Kuo Tian
Liquefaction of EICP-Treated Sand with Fabric Anisotropy
Yang Xiao, Lei Zhang, Jinquan Shi, Jian Hu and T. Matthew Evans
Technical Notes
Effect of Failure-Inducing Cyclic Loading on Pile Capacity in Sand
Yaru Lv, Jieming Hu, Barry M. Lehane and Dianjun Zuo
Near-Field Effects on the in situ Estimation of Shear-Wave Velocity and Damping Ratio from MASW Tests
Mauro Aimar and Sebastiano Foti
Géotechnique
Volume 75, Issue 13 (December 2025) / https://www.emerald.com/jgeot/issue/75/13

목차
Research Articles
Limit-state solutions for the active earth pressure behind walls rotating about the base
David Perozzi; Alexander M. Puzrin
Effect of salinity on the effective stress of compacted bentonites
Vicente Navarro; Laura Asensio
Engineered bioclogging in sands: comparison of microbially induced and enzyme-induced biopolymer formation
Yong-Min Kim; Tae-Hyuk Kwon
A microscopic interpretation of hysteresis in the water retention curve of sand
Yosuke Higo; Ryunosuke Kido
Modelling the piping-assisted erosion of clay barriers
Huaxiang Yan; Majid Sedighi; Andrey Jivkov; Abdelmalek Bouazza
Exploring the micro-to-macro response of granular soils with real particle shapes by way of μCT-aided DEM analyses
Yang Li; Masahide Otsubo; Vasileios Angelidakis; Reiko Kuwano; Sadegh Nadimi
Use of shells for the mechanical stabilisation of sediments: a valuable geomechanical perspective?
Rossella Petti; Claudia Vitone; Maurizio Iler Marchi; Michael Plotze; Alexander Puzrin
Modified Cam Clay bounding surface hyper-viscoplastic model
Davood Dadras-Ajirlou; Gustav Grimstad; Seyed Ali Ghoreishian Amiri; Samson Abate Degago; Guy T. Houlsby
Footprints on the beach: visualising dilation-induced air entry
F. Parera Morales; G. A. Siemens; M. Mckellar; N. M. Pinyol; E. E. Alonso; W. A. Take
Two-dimensional experimental assessment of interaction energy-induced suffusion in sand-clay mixtures
Jongmuk Won; Incheol Joo
Introducing tunnel kinematic constraints into an elastic continuum formulation of tunnel-soil-pipeline interaction
Assaf Klar; Andrea Franza; Mingliang Zhou; Hong-Wei Huang
Maximum shear modulus anisotropy of rooted soils
Ali Akbar Karimzadeh; Anthony Kwan Leung; Zhiwei Gao
Influence of grading in compacted tailings behaviour: towards resilient design
Alexia Cindy Wagner; Joao Vitor de Azambuja Carvalho; Hugo Carlos Scheuermann Filho; Nilo Cesar Consoli
Monotonic and cyclic lateral loading of piles in low- to medium-density chalk
R. A. McAdam; R. M. Buckley; F. Schranz; B. W. Byrne; R. J. Jardine; S. Kontoe; T. Liu; K. Vinck; J. J. Crispin
On the development of effective heave pressure in deep excavations
Johannes Tornborg; Mats Karlsson; Jelke Dijkstra; Minna Karstunen
Drained and undrained behaviour of a sandy silt gold tailings under general multiaxial conditions
Riccardo Fanni; David Reid; Andy Fourie
A consistent derivation of soil stiffness from elastic wave speeds
D. M. Riley; I. Einav; F. Guillard
Effect of episodic pre-failure cyclic loading on whole-life geotechnical properties of soft clays
Noor Laham; Katherine Kwa; Yusuke Suzuki; David White; Susan Gourvenec
Interaction between tunnel-boring machines and heavily squeezing purely cohesive grounds
Thomas Pferdekamper; Apostolos Vrakas; Georgios Anagnostou
Integration of hyperplastic models in strain space
S. A. Ghoreishian Amiri; G. Grimstad; D. Dadras-Ajirlou
Small-strain stiffness anisotropy of soils subjected to internal erosion
Teing Teing Tan; Ali Akbar Karimzadeh; Anthony Kwan Leung
Physical and theoretical modelling of embedded mooring line-seabed interaction in sands
Katherine Kwa; Conleth O’Loughlin; David White; Colm O’Beirne; Sebastiaan Frankenmolen
Potential of low-permeability barriers to mitigate backward erosion piping
Lexin Li; Vera Van Beek; Timo Heimovaara; Anne-Catherine Dieudonné
Mathematical model for piled embankments on saturated soft clay
Viviana Mangraviti; Jelke Dijkstra; Luca Flessati; Claudio Di Prisco
Anisotropic constitutive modelling of rooted soils
Ali Akbar Karimzadeh; Zhiwei Gao; Anthony Kwan Leung
Canadian Geotechnical Journal
Volume 62, 2025 / https://cdnsciencepub.com/toc/cgj/62

목차
Research Articles
Assessing water position through distributed temperature sensing using Rayleigh-based optical frequency-domain reflectometry: a laboratory feasibility study
Ashis Acharya, Daiki Tanimura, Chao Zhang, Fumihiko Ito, ... Tetsuya Kogure
Poromechanical analysis of regional frozen ground responses under heat exchanger operations
Kian Khaksar, Biao Li
Analysis of the ultimate uplift resistance and progressive failure process of strip plate anchors in marine sensitive clays: a FE analysis based on micropolar continuum theory
Wencheng Wei, Hongxiang Tang
A new and simple hydraulic characteristic model of unsaturated rooted soils considering pore creation and non-uniform pore occupation
Yan-peng Cui, Qing-yi Mu, Yan-jun Shen, Anthony Kwan Leung, Jian-bing Peng
Evaluation of cementation effects on swelling properties of bentonite buffer material using natural analogue
Daichi Ito, Hailong Wang, Hideo Komine
Coal-derived char for durability improvement of cement stabilized soil under freeze-thaw, wet-dry, and sulfate attack
Hua Yu, Priyanka Joshi, Chooikim Lau, Kam Ng
Consolidation of clay slurry under very low stresses: from novel oedometer apparatus invention to nonlinear
consolidation characteristics and finite strain modelling
Peng-Lin Li, Zhen-Yu Yin, Ding-Bao Song, Ze-Jian Chen, Jian-Hua Yin
Discussion of “An evaluation of p-y curves for fatigue analysis of offshore piles and conductors” by Guevara, M. and Doherty, J.P. Watson, P.G. and White, D.J.
W.O. McCarron
Data-driven recovery of incomplete geotechnical dataset using low-rank matrix completion
Zheng Guan, Yu Wang, Kok-Kwang Phoon
Analysis of unbalanced forces on large shield cutterhead in karst composite strata
Zhaoyang Deng, Xutian Zhang, Kaiyuan Ge, Pengfei Ma
Quantification and practical solution for bottom boundary effects on long-term permafrost models
C.R. Ross, R.A. Beddoe, G.A. Siemens
Reply to the discussion on our paper “Material-specific interpretation of the state parameter from drained cone penetration test”
by Mohammad RazaviNasab, Katia Boschi, and Marcos Arroyo
Mason Ghafghazi
Undrained cavity expansion-contraction analysis in CASM and its application for pressuremeter tests
Guo-Yao Li, Pin-Qiang Mo, He Yang, Hai-Sui Yu, Yong-Jun Qin
Settlement characteristics and evaluation approach of embankment widening over soft clay
Gang Zheng, Jiawei Wang, Haizuo Zhou, Boyang Xia, Phu Doanh Bui
Slope stability prediction using multi-stage machine learning with multi-source data integration strategy
Yunmin Chen, Jiateng Kong, Yihuai Lou, Xinke Zhang, ... Daosheng Ling
Effects of fines content and stress history on surface erosion of cohesive soils
Yunjie Lin, Cheng Lin
A numerical study of deep excavations adjacent to existing tunnels: integrating CPTU and SDMT to calibrate soil constitutive model
Fengwen Lai, Franz Tschuchnigg, Helmut F. Schweiger, Songyu Liu, ... Guojun Cai
Impact of sample preparation on erosion characteristics and subsequent mechanical behaviour of gap-graded soils: an imagingbased analysis
Meysam Mousavi, Mahdi M. Disfani, Jay R. Black, Amirhassan Mehdizadeh
The effect of thermoactivated pile spacing on the thermo-mechanical response of energy soldier piled walls--extended
numerical investigation
Luis Villegas, Raul Fuentes, Guillermo A. Narsilio
Enhancement and assessment of large vision models for 3D particle reconstruction from X-ray tomography
Ruidong Li, Zhen-Yu Yin, Shaoheng He, Brian Sheil
Prediction of impulse waves generated by the potential failure of large deposits in the Rumei Reservoir, Lancang River, China
Yuhao Liu, Guoxiang Tu, Bo Luo, Hao Tang, Qifeng Luo
Discussion on “Material-specific interpretation of the state parameter from drained cone penetration test” by Mohammad Mozaffari and Mason Ghafghazi
Mohammad RazaviNasab, Katia Boschi, Marcos Arroyo
Evolution of grading and particle crushing of rockfills upon shearing and over creeping in large-scale triaxial tests
Mengcheng Liu, Xuan Chen
A CSS surface-based THM bounding constitutive model for volumetric behavior of bentonite
Yang Wang, Wei-Min Ye, Qiong Wang, Yong-Gui Chen
Effect of progressive wetting on permanent deformation of fouled ballast under cyclic loading
Shihao Huang, Yu Qian
A new flow-path energy-based approach for the preliminary design of debris flow risk mitigation measures: the real case of Favazzina
Marilene Pisano, Pasquale Visalli, Saeid Moussavi Tayyebi, Manuel Pastor, Nicola Moraci
The effects of desiccation crack and seasonal variation on hydrological response of compact clay embankment
Arwan Apriyono, Yuliana Yuliana, Viroon Kamchoom, Anthony Kwan Leung, Apiniti Jotisankasa
Experimental study on multi-parameter performance differences of coal with different rockburst tendencies
Yanhui Li, Jianbiao Bai, Xiangyu Wang, Xiaoqing Wang, Xiangqian Zhao
Long-term soil thermal imbalance analysis of the energy pile considering ambient thermal boundary
Wang Xi, Yong Zhao, Shijin Feng, Hongxin Chen, Jincheng Fang
Multiscale mechanical behaviour of sand-steel structure interface for deep underground space
Yue-Hui Sun, Han-Lin Wang, Fan-Yan Meng, Cheng-Shuang Yin, Xiang-Shen Fu
Ex situ hyperspectral sensing and machine learning for tailings characterization
Joseph Bindner, Christopher Bareither, Joseph Scalia
Responses of ice-soil mixtures to ice melting
Z.D. Xu, M. Kamali Zarch, H.J. Wang, Z.X. Zeng, L.M. Zhang
Experimental investigation of marine soil stabilization with recycled aggregates and MgO: implications for CO2sequestration
Yunlu Hou, Chikezie Chimere Onyekwena, Qi Li
A concept of CSS surface for describing the thermo-mechanical volume change of unsaturated bentonite
Yang Wang, Wei-Min Ye, Qiong Wang, Yong-Gui Chen
Use of rigid inclusions for foundations of container yards
Hao Chen, Shifan Wu, Stephen Lim, Tiancheng Song, Jian Chu
Modelling pile foundations under biaxial loading with a plasticity-based p-y methodology
W.O. McCarron
Performances of a large-scale deep excavation with multi-support types and zoned excavation technique in Shanghai soft soil
Yingjie Jing, Lin Li, Jingpei Li, Haohua Chen
Uncertainty assessment of effective friction angle of non-cohesive materials combining data from cone penetration and shear tests
Julia Sorgatz, Andreas Janzen, Johan Spross
Computed tomography-driven analysis of particle breakage using a coupled FDM-DEM approach
Mengmeng Wu, Yuze Sun, Xianghao Situ, Jianfeng Wang, Zhen-Yu Yin
International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences
Volume 198 In progress(February 2026) / https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/international-journal-of-rock-mechanics-and-mining-sciences/vol/198/suppl/C

목차
Research Articles
On the thermal effects of mechanical behavior in the Callovo-Oxfordian claystone
Chuanrui Wang, Shouyi Xie, Jian-Fu Shao, Minh-Ngoc Vu, Christophe de Lesquen
Failure behaviour simulation of transversely isotropic rocks considering realistic grain structure and bedding plane morphology
Renjie Wu, Haibo Li, Guorui Feng, Yuxia Guo, Chong Yu
Normal deformability of rough rock joints - a predictive analytical model based on Persson's theory of contact
Yue Cui, Yingchun Li, Yang Xu
A novel hydro-mechanical-chemical coupled experiment for unconventional hydrocarbon production evaluation
Meng Meng, Marcus Wigand, Luke P. Frash, Mohmad M. Thakur, ... James W. Carey
A multi-processes phase-field model for CO2 phase change fracturing
ZiHan Zhang, Hao Yu, Bo Li, Wei Cheng, ... HengAn Wu
A method for mechanical properties identification of nonlinear joints based on deep learning in time-frequency domain
L.F. Fan, M.Z. Ye, Q.H. Yang, X.L. Du
Fragmentation and energy dissipation in rockfall: Effects of block shape and non-collinear impact dynamics
Maddalena Marchelli, Davide Ettore Guccione, Anna Giacomini, Olivier Buzzi
A novel Bayesian network-enhanced 3D digital rock mass rating (DRMR3D) system for large-scale rock mass characterization using photogrammetry
Wentao Xu, Shihuai Zhang, Jie Kuang, Longchuan Deng, ... Xiaozhao Li
Predicting rockfall hazard with deep learning: Latent feature extraction from geological layers
Guilherme Barros, Klaus Thoeni, Pablo Moscato, Jinsong Huang, Anna Giacomini
Frictional evolution of rock fractures across mineralogical contrasts
Kai Guo, Nuwen Xu, Wei Wu
Nonlinear progressive failure mechanism and shear strength model of deeply buried jinping marble under direct shear
Chunfeng Ye, Cunbao Li, Hengjun Chen, Fei Wu, ... Heping Xie
Soils and Foundations
Volume 65, Issue 6 In progress (December 2025) / https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/soils-and-foundations/vol/65/issue/6

목차
Research Articles
Upcycling rice husk biowaste to improve cement-based peat soil stabilization
Zhiliang Wang, Jiangpeng Cai, Miao Li, Linfang Shen
Triaxial mechanical properties and microstructure of Tianjin clay stabilized with fly ash-based geopolymer
Rui Jia, Zhenxing Chu
Investigation on the lateral performance of new piles in sand sites containing existing piles and shallow cement-treated backfill
Hongjiang Li, Tianyuan Wu, Songyu Liu, Liyuan Tong, ... Wenyuan Liu
Shear wave velocity based prediction of CaCO3content and UCS in MICP-treated soils with different particle sizes
Yuhang Zeng, Hui Xu, Yubin Zheng, Hao Zheng, Ping Chen
Dewatering of bentonite slurries by the combined use of polymeric ferric sulfate (PFS) and optimized flocculation-preloadingelectroosmosis (FPE)
Zhijia Xue, Qiquan Deng, Xin Hou, Xiao Lu, ... Zhifeng Tian
Normal and seismic performance of backfill sand enhanced with biomass waste-derived materials under road pavement
Yinglong Liu, Maliki Otieboame Djandjieme, Kimitoshi Hayano, Hiromoto Yamauchi, Cong Li
Numerical and experimental study on the seismic performance of caisson foundations
Sohail Ahmad, Tianbo Peng, Muhammad Salman Khan
Interface clogging between soil and attenuation layer of embankment based on LBM-DEM coupled numerical method
Xudong Zhang, Atsushi Takai, Tomohiro Kato, Takeshi Katsumi
Field investigation of steel screw micropiles under axial loads in cohesionless and cohesive soils
Joao Batista de Oliveira Liborio Dourado, Lijun Deng
Microstructural characterisation of foam-induced porosity in lightweight cemented soils using X-ray micro-tomography
F. Ferriero, L. Perrotta, L. Pappalardo, G. Buono, ... G. Russo
Large-area slope stability analysis: Performance comparison of three-dimensional limit equilibrium methods
Daichi Sugo, John Y. Choe, Saneiki Fujita, Nilo Lemuel J. Dolojan, ... Shuji Moriguchi
Technical Note
Microscopic investigation into density dependence of water retention characteristics of sand during drying-wetting process Ryunosuke Kido, Yosuke Higo, Shizuka Eshiro
Wenyue Zhang, Mai Tabuchi, Tomotaka Yoshikawa, Akihiro Takahashi
Special Issue on the 3rd International Symposium on Risk Assessment and Sustainable StabilityDesign of Slopes - ISRSS-Sendai 2022
Dynamic analysis of wave propagation due to pile installation using numerical simulations
Maliha Tasnim Tilat, Sascha Henke
Geostatistical-learning-based site-optimum 3D integration of borehole logs and geophysical data in urban area in South Korea
Joung-Woo Han, Mingi Kim, Han-Saem Kim, Taek-Kyu Chung, Choong-Ki Chung
Enhanced microstructural analysis of black cotton soil stabilized through rice husk ash integration
Ankur Abhishek, Anasua GuhaRay, Toshiro Hata
임환희
한국원자력안전기술원 구조부지평가실 선임연구원
(hwanhui@kins.re.kr)
논문집 개요 소개
논문집 개요 소개 | 2025년 12월 제 41권 6호
필댐 월류피해 및 원인에 대한 지반공학적 관점의 고찰
유 찬(정회원, 경상국립대학교 지역시스템공학과 교수, chanyu@gnu.ac.kr)
실제 흙댐 월류발생 사례에 대해서 현장 조사, 자료 수집 및 분석을 실시하였다. 대상 흙댐은 중형의 농업용 저수지로서 1975년에 준공되어 대략 50년 동안 운영되어 왔으며, 2023년 9월 태풍의 영향으로 월류가 발생되어 하류 주민들에 대한 대피명령이 내려졌고, 제체 하류사면이 코어층 깊이까지 침식이 진행되었다. 그러나 계속되는 강우와 추가적인 제체 붕괴의 우려로 손상된 하류 사면은 신속하게 복구해야 했고, 이로 인하여 정확한 지반공학적 조사와 시험이 불가능 했다. 따라서 본 논문에서는 사고발생 직후 참여한 현장 육안조사 및 영상자료 그리고 저수위 계측자료를 분석하여 월류발생 전후 상황에서 제체의 침식발생과 붕괴 직전까지 상황을 기존 연구 자료들과 비교/분석한 내용을 정리하였다. 연구결과 하류사면 보호 식생, 보수공사기간에 이루어진 제체 내 그라우팅 보강, 월류 속도, 그리고 월류지속 시간의 복합적인 영향이 긴급 월류 상황에서도 제체의 완전 붕괴가 발생하지 않은 데 기여했을 것으로 추정된다. 그러나 정보 부족으로 인해 각각의 단일 요소의 영향을 정량화하는 데에는 한계가 있었다. 이 결과는 기존의 댐 설계의 각 요소 중 하나라도 부족했다면 더 심각한 피해가 발생했을 가능성을 시사한다. 또한 언급된 다양한 요소들이 설계 및 시공에 충실히 반영 및 시공되었고, 지속적인 유지관리와 보수보강이 사고 피해를 최소화하였을 것으로 추정된다.
내진설계를 위한 지반분류별 전단파속도 분포 특성 및 깊이에 따른 전단파속도의 변동계수 모델식 제안
오현주(정회원, 충남대학교 토목공학과 박사과정)
배두산(정회원, 충남대학교 토목공학과 석사)
박형춘(정회원, 충남대학교 토목공학과 교수, civilman@cnu.ac.kr)
지반의 전단파속도(Vs) 주상도는 내진설계에 있어 지진파의 증·감폭 특성을 결정짓는 핵심 요소이다. 그러나 시간·경제적 제약으로 인해 충분한 수의 지반조사를 수행하기 어려워, 실무에서는 제한된 횟수의 조사를 통해 얻은 전단파속도 주상도의 평균을 대표값으로 사용하게 된다. 이는 지반 물성치의 공간적 변동성을 고려하지 못해, 지진 시 실제 지반 거동과 해석 결과 사이에 차이를 유발할 수 있다. 이러한 불확실성은 확률론 기반의 신뢰성 해석을 통해 반영할 수 있으며, 통계적 방법을 활용해 전단파속도 랜덤 필드를 생성하고, 이를 바탕으로 몬테카를로 시뮬레이션이나 변동계수(COV)를 활용한 해석을수행할 수 있다. 본 연구에서는 세종특별자치시 부지조성 단계에서 수행된 160개의 다운홀 시험 데이터를 활용하여, 토층 평균 전단파속도(Vs,soil)를 기준으로 S2 지반(55개), S3 지반(16개), S4 지반(89개)으로 분류하였다. 이후 각각에 대해 존재 가능한 전단파속도 주상도 243개(S2), 193개(S3), 243개(S4)를 생성하였으며, 이를 바탕으로 지반분류별 전단파속도 분포 특성을 평가하고, 깊이-전단파 속도 모델식을 제안하였으며, 신뢰성 기반 해석에 활용 가능한 깊이별 전단파속도 변동계수 모델식을 제안하였다.
터널갱구부 비전기 뇌관발파시 발파소음의 전파특성 및 영향평가 방법
오진욱(정회원, 대진대학교 토목환경공학과 박사과정)
신유석(정회원, 대진대학교 토목환경공학과 박사과정)
이강일(정회원, 대진대학교 스마트건설환경공학과 교수, kilee@daejin.ac.kr)
최근 들어 철도노선의 연장, 광역급행철도 신설 등으로 도심지의 터널시공을 위한 발파가 빈번해짐에 따라 발파소음수준의 저감을 위한 연구도 활발하게 수행되어 왔다. 그러나 터널 입구에 발파 및 방음 시스템을 다르게 설치할 경우 발파 지점과의 거리에 따라 소음 수준 감소 효과가 달라질 수 있음에도 불구하고 이에 대한 연구 결과가 부족하여 효과적인 방음 시스템선정에 문제가 있었다. 또한 소음영향평가 수행시 발파소음의 예측방법이 상이하기 때문에 발파소음수준 예측 및 발파소음의 소음 규제기준 초과여부 결정에 대한 논란도 지속되고 있다. 이에 본 연구에서는 이와 같은 문제를 해결하기 위해 방음시스템을 달리 설치한 국내 3개소의 터널갱구부를 대상으로 비전기식 뇌관 시험발파를 수행하였다. 연구결과, 철재 프레임과 판넬로 구성된 방음벽이 타이어매트와 같은 연성 재질로 구성된 방음문보다 발파소음의 저감에 효과적이었고, 터널갱구부에 대한 발파소음 예측은 Lee(2003)과 EX(2009)의 예측방법이 좀 더 적합한 것으로 분석되었다.
현장시험 분석을 통한 말뚝지지 전면기초의 하중분담 특성
홍석우(정회원, 동의대학교 토목공학과 교수, hongswoo@deu.ac.kr)
서영훈(정회원, 한주이엔씨(주) 대표이사, 공학박사)
본 연구의 출발은 앞으로 지어질 대형 구조물에 대하여 지금보다 안정성을 확보하면서도 경제성이 확보되는 기초공법에 대한 고민에서 시작되었으며, 국내 대형 구조물 현장에서 실시된 대형평판재하시험을 실시한 네 곳의 자료와 유한요소해석을 통해 분석하여 8종류의 지반강도정수를 산정하였다. 산정된 지반강도정수의 조건으로 4가지 말뚝 직경과 5가지의 간격비로하중분담률을 분석하였으며, 지반강도정수의 각 매개변수 점착력, 내부마찰각, 변형계수가 하중에 따른 지반의 변형에 미치는 영향을 파악하기 위해 개별적 검토를 실시하였으며, 검토 결과 지반의 침하에는 변형계수가 가장 큰 직접적인 매개변수임을 확인 할 수 있었다. 본 연구에서 제안한 식을 말뚝지지 전면기초의 실무 설계에 적용하기 위하여 가장 중요한 변수인 변형계수의 정확한 적용을 위해 사례 현장의 공내재하시험 변형계수 값과 대형평판재하시험 변형계수 값을 직접 비교한 결과를 정리하였으며, 그 결과가 258%~618%의 큰 편차가 있는 것으로 확인되었다. 대형평판재하시험과 공내재하시험과의 변형계수 상관관계에 대한 추가적인 시험을 통해 명확한 이론이 정립이 되면 본 연구에서 제안된 식을 이용한 말뚝지지 전면기초 설계를 보다 정확히 할 수 있을 것으로 판단된다.
수치해석을 통한 수평하중에 저항하는 복열 마이크로파일의 지지특성 및 적정 설치조건
김무연(정회원, ㈜아이원이앤씨 대표이사)
황승민(정회원, 동국대학교 건설환경공학과 학사과정)
이강일(정회원, 대진대학교 스마트건설환경공학과 교수, kilee@daejin.ac.kr)
기존 또는 신설 구조물 기초의 하부에 설치되는 300mm 이하의 마이크로파일은 군말뚝형태로 설치된다. 그리고 이 파일은 다양한 설치조건으로 지반에 설치할 수 있고, 기존 파일(PHC파일, 강관 파일)과 달리 다양한 설치각도로 시공할 수 있다. 즉, 기초상부에 작용하는 하중에 마이크로파일이 효과적으로 저항하도록 다양한 설치조건으로 시공할 수 있다. 기존 연구결과를 통해 알 수 있듯이 기초상부에 수평하중이 작용하는 경우 경사파일이 효과적이다. 그럼에도 수평하중에 저항하기 위해 설치하는 마이크로파일은 기존 파일과 같이 직항으로 설치한다. 이에 본 연구에서는 다양한 설치조건 고려한 복열 마이크로파일의 수평지지특성을 평가하고 적정 설치간격과 설치각도를 제안하기 위해 수치해석을 수행하였다. 그리고 적정설치간격은 파일직경의 4.7배 이상이고, 설치각도 -15°≤θ≤+30°인 경우 복열 마이크로파일의 수평지지력이 직항인 복열 마이크로파일보다 증가함을 연구결과를 통해 확인하였다.
국내 지반조건을 반영한 철도 지하 박스 구조물의 동적 거동 분석
이유성(정회원, 가천대학교 토목환경공학과 석사과정)
김석중(정회원, 한국건설기술연구원 지반연구본부 수석연구원)
유민택(정회원, 가천대학교 토목환경공학과 조교수, mintaekyoo@gachon.ac.kr)
본 연구는 지진 발생 시 한국의 지반 조건에 맞는 지하 철도 지하 박스 구조물의 내진 성능을 평가하기 위한 2차원 유한요소 모델을 개발하였다. 제안된 모델은 1차원 부지응답 해석 프로그램인 DEEPSOIL을 활용하여 비선형 지반의 동적 응답을 비교 및 검증하였으며, 지하 박스 구조물의 형상 및 제원은 실제 한국의 개착식 대합실의 시설 계획을 기반으로 설정하였다. 본 모델을 통하여 입력 지진파의 특성, 지하 박스 구조물의 근입 깊이, 지반의 전단파 속도 등 다양한 변수에 따른 동적 거동 특성을 분석하였다. 그 결과, 입력 지진파의 주파수 성분과 지반의 강성에 따라 구조물의 동적 응답 특성이 상이하게나타났으며, 지반의 강성이 낮고 지하 박스 구조물의 근입 깊이가 깊어질수록 측벽 및 상부 슬래브에 작용하는 휨 모멘트가 증가하는 경향을 보였다.
직접전단시험을 통한 섬유 및 시멘트 슬러리 기둥이 혼합된 소형 모래 공시체의 강도 특성
문홍득(정회원, 경상국립대학교 건설환경공과대학 건설시스템공학과 교수)
김종엽(비회원, 경북대학교 공과대학 건설환경에너지공학부 대학원생)
왕차오(비회원, 경북대학교 공과대학 건설환경에너지공학부 대학원생)
성희영(비회원, 경북대학교 공과대학 건설환경에너지공학부 대학원생)
우승욱(비회원, 경북대학교 공과대학 건설환경에너지공학부 대학원생)
박성식(정회원, 경북대학교 공과대학 토목공학과 교수, sungpark@knu.ac.kr)
자연에는 다양한 식생이 토사 내에 뿌리를 내리고 지반의 물리적 안정성에 기여하고 있다. 대부분의 기존 연구는 섬유를 모래나 점토에 분산 혼합하는 방식을 사용하나, 본 연구에서는 전단 방향과 직각으로 기둥 형태로 일정하게 분산 매립하였다. 가는 섬유 다발과 시멘트 슬러리 기둥과 같이 강도와 강성이 서로 다른 물질을 모래에 혼합시켜 직접전단시험을 수행하였다. 두 종류의 상대밀도와 세 종류의 섬유비 그리고 섬유 다발과 동일한 부피의 시멘트 슬러리 기둥의 분포도에 따른 전단강도 변화를 연구하였다. 또한, 섬유 다발과 시멘트 슬러리 기둥을 복합적으로 매립하여 각각의 재료가 모래의 전단강도에 미치는영향을 분석하였다. 그 결과, 섬유 다발과 시멘트 슬러리 기둥 모두 모래의 최대전단응력을 증가시켰다. 모래의 내부마찰각은 섬유로 보강한 경우 상당히 증가하였으며, 느슨한 경우는 35°에서 38°로, 조밀한 경우는 38°에서 최대 41°까지 증가하였다.074소식통점착력은 시멘트 슬러리로 보강한 경우 느슨한 모래는 0 kPa에서 190 kPa로, 조밀한 모래는 11 kPa에서 최대 230 kPa까지 증가하였다. 특히 동일한 섬유비에서 더 많은 지점에 나누어 매립하는 것이 모래의 전단강도를 더 증가시켰다. 그리고, 두재료를 복합적으로 모래에 사용한 경우 각각의 특성이 모두 발현되었으며, 즉 모래의 내부마찰각과 점착력이 모두 증가하는 효과를 얻을 수 있었다.
비탈면 식생 유무에 따른 강우침투에 의한 붕괴 민감도 분석
김재홍(정회원, 동신대학교 토목환경공학과 부교수)
유형식(정회원, (주) 영진엔지니어링 대표이사)
최용준(정회원, 동신대학교 토목환경공학과 박사과정)
김태완(정회원, 동신대학교 토목환경공학과 박사과정, kyoug222@naver.com)
산비탈에 벌목으로 인한 비탈면 붕괴가 발생하는 원인을 확인하고자 수풀지역과 벌목지역이 혼재된 사면을 대상으로 함수비 센서를 설치하여 장마철 강우량 침투를 분석하였다. 본 연구에서는 식생 유무에 따른 체적함수비 증가 기울기(VWCG;Volumetric Water Content Gradient)와 유효누적강우량(ECR; Effective Cumulative Rainfall)을 활용하여 표층붕괴를 판단하는 방법을 고찰하였다. 분석 절차는 다음과 같다. 먼저, 무선센서네트워크(WSN; Wireless Sensor Network) 기반 실시간 계측시스템을 구축하여 구역별 토양 수분 함량을 측정하고 이를 토대로 체적함수비 증가 기울기(VWCG)를 산정하였다. 이후 산정된 VWCG와 ECR 값을 이용하여 표층붕괴와의 상관성을 검토하였다. 분석 결과, 체적함수비 증가기울기(VWCG)와 유효누적강우량(ECR)이 동시에 높은 구간에서 실제 붕괴가 발생하였다. 수풀지역은 주로 VWCG 0.1이하, ECR 60 mm 이하 범위에 분포하였으며, 벌목지역은 VWCG 0.2 이상, ECR 40~70 mm 범위에 집중적으로 나타났다. VWCG와 ECR이 높을수록 붕괴 발생 가능성이 증가하였으며, 이는 식생 분포가 임계값의 변동에 직접적인 영향을 미치는 것으로 확인되었다. 특히, VWCG ≥ 0.3 및 ECR ≥ 80 mm 조건에서 붕괴 발생이 집중적으로 관찰되어 본 연구에서는 이를 표층붕괴 조기경보를 위한 주요 임계값으로 제시하였다.
지하수 흐름 조건에서의 인공동결시스템의 동결거동 평가 및 윈도우 발생에 대한 임계 유속 평가
고규현(정회원, 국립금오공과대학교 건축토목환경공학부 부교수, gyuhyungo@kumoh.ac.kr)
양수웅(비회원, 국립금오공과대학교 건축토목환경공학부 학사과정)
고기은(비회원, 국립금오공과대학교 건축토목환경공학부 학사과정)
우석윤(비회원, 국립금오공과대학교 건축토목환경공학부 학사과정)
인공동결공법은 도심지 지하 굴착 시 활용되는 연약지반 보강기법으로서 선진국을 중심으로 최근 들어 활발히 적용되고 있다. 하지만 빠른 지하수 침투 환경을 가진 지반 조건에서는 동결관 주변의 열전달이 지하수 유동에 의해 영향을 받으면서 공법 적용에 많은 어려움이 초래된다. 본 연구에서는 빠른 지하수 흐름 조건에서의 지반 동결 거동을 평가하기 위해 실내모형토조시스템을 자체 개발하였고, 다양한 지하수 유속 별 지반 동결 실험을 수행하였다. 토조실험을 통해 얻어진 데이터를 Python 기반의 후처리 기법을 통해 육안 관찰이 어려운 지반 내부의 동결 벽체 형성 과정을 시각화하고, 동결벽체의 양상을 확인하였다. 또한, 동결 벽체 주변 윈도우 발생을 유발하는 임계 지하수 유속의 범위를 제시하였다.
마이크로파 소결 블록 크기 향상을 위한 시스템 구성 영향 평가
진현우(정회원, 한국건설기술연구원 미래스마트건설연구본부 수석연구원, hyunwoo.jin@kict.re.kr)
김영재(비회원, 한국건설기술연구원 미래스마트건설연구본부 수석연구원)
이장근(정회원, 한국건설기술연구원 미래스마트건설연구본부 선임연구위원)
달 표면에서 얼음 형태의 물, 헬륨-3과 같은 에너지자원이 발견됨에 따라 달은 심우주 탐사를 위한 전초기지로 주목받고 있다. 지속 가능한 심우주 탐사를 위해 현지자원 활용 개념이 주목받음에 따라, 현지재료인 월면토 고형화 기술의 활용 가능성이 증대되고 있다. 본 연구에서는 기존에 선행된 기초연구들에서 얻어진 결과를 토대로 9 kW 급 마이크로파 소결로를 활용해 가로, 세로, 높이가 각각 약 200 mm, 200 mm, 60 mm인 소결 블록을 제작하였다. 이 과정에서 마이크로파 출력량 및 출력 위치, 추가 보조가열재 조각 배치 등의 소결 시스템 구성을 비롯해 소결온도가 균질한 마이크로파 소결 블록 제작에 미치는 영향을 평가하였다. 그 결과 마이크로파 출력 위치와 관계없이 2.1 kW의 출력, 양 측면 보조가열재 조각 배치, 소결온도 1,050°C에서 균질한 소결 블록이 제작되었다. 그러나 코어링된 시편에서 측정된 물리적 및 역학적 특성을 분석한 결과 마이크로파 출력 위치가 후면인 경우 다른 위치에서 출력된 것보다 상대적으로 소결 효율이 낮은 것으로 나타났다.
소규모 지반 물성 자료를 활용한 IW 및 어닐링 기반 좌표 예측 기법의 비교 연구
윤형구(정회원, 대전대학교 재난안전공학과 교수, hyungkoo@dju.ac.kr)
지반의 미측정 지점의 데이터를 유추할 수 있는 크리깅 기법은 관측 지점 간 거리가 멀어질수록 상관성이 급격히 감소하여 신뢰성이 낮은 한계를 보인다. 본 연구의 목적은 소규모 지반조사 데이터인 토심을 이용하여 공간적 예측 정확도를 향상시키기 위한 Independent Weighted(IW) 및 어닐링(Annealing) 기반으로 좌표 예측을 수행하는 것이다. Dynamic Cone Penetration Test(DCPT)를 통해 총 23개 지점에서 실측된 토심 데이터를 활용하였으며, 데이터의 희소성을 보완하기 위해 Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique(SMOTE)와 Adaptive Synthetic Sampling(ADASYN) 알고리즘을 적용하였다. IW는 각 격자점의 토심을 거리 가중 평균으로 계산하여 초기 예측을 수행하였고, 어닐링은 IW 결과를 초기 해로 설정한 후 확률적 스왑 연산을 반복 수행하여 전체 오차를 최소화하였다. 비교 결과, 어닐링 적용 후 예측 오차(RMSE)는 IW대비 약 25~30% 감소, 정규화된 오차합(Energy)은 약 40% 이상 감소하였다. 또한 성능을 평가할 수 있는 6가지 지표 값도 제시하였으며, 모두 신뢰성이 향상된 결과를 보여줬다. 해당 연구에서 사용한 방법인 IW 및 Annealing 기법은 소규모 지반조사 환경에서도 토심 분포를 현실적으로 재현할 수 있는 효율적이고 신뢰성 높은 예측 방법임이 검증되었다.
도심지 교차상관 탄성파 간섭법 적용을 위한 MUSIC 빔포밍 기반 인라인 소스 선택 기법 연구
황선호(정회원, 건국대학교 사회환경공학부 석사과정)
신창호(정회원, 건국대학교 사회환경공학부 석사과정)
구태서(정회원, 건국대학교 사회환경공학부 부교수, tsku@konkuk.ac.kr)
도심 교통잡음(상시미동)은 불균등성과 비정상성이 강해, 이를 단순 적층(stacking)에 기반한 교차상관 탄성파 간섭법에 적용할 경우 주파수-위상속도 스펙트럼(Frequency - phase velocity spectrum)의 불연속과 편향을 유발한다. 본 연구는 Multiple Signal Classification(MUSIC) 빔포밍을 이용해 주파수별 도래각(Direction of arrival, DOA)을 추정하고, 배열축과 정렬된(in-line) 섹터만 선택한 뒤 역 단시간 푸리에 변환(Inverse Short-Time Fourier Transform, ISTFT)으로 방향성 필터링 파동장을 재구성하는 개념적 절차를 제안한다. 서울 소리공원에서 제안 기법, MASW, 기존 교차상관 탄성파 간섭법을 비교한 결과, 제안 기법이 분산곡선의 불연속성을 해결하고 역산된 기반암 심도(14.4 m) 및 속도(1,302 m/s) 추정에서 가장 높은 정확도를 보였다. 반면 MASW(15.6 m, 783 m/s)와 기존 교차상관 탄성파 간섭법(11.2 m, 1,371 m/s)은 기반암 심도 예측 오차가 크거나 속도를 과소평가하였다. 이는 현장 적용 결과, 저주파 재현성과 방위의 일관성이 향상되어 MUSIC 기반 인라인소스선택이 도심 환경 기반암 탐지 정확도를 크게 향상시킴을 입증한다.
1D 및 2D 수치해석을 통한 포항 지역 액상화 가능 지반의 지반응답 특성 비교
문준성(정회원, 부산대학교 사회환경시스템공학과 석사과정)
김진만(정회원, 부산대학교 사회환경시스템공학과 정교수, jmkim@pusan.ac.kr)
손수원(정회원, 경일대학교 건축토목공학과 조교수)
윤종찬(정회원, 부경대학교 지속가능공학부 토목공학전공 박사후 연구원)
박윤호(비회원, 부산대학교 사회환경시스템공학과 석사과정)
서정원(비회원, 부산대학교 사회환경시스템공학과 석사과정
본 연구에서는 2017년 포항지진 피해지역을 대상으로 SHAKE2000, DEEPSOIL, PLAXIS 2D를 이용한 1차원 및 2차원 지반응답해석을 수행하였다. 동일한 입력 조건하에서 반복전단응력비(CSR), 반복저항응력비(CRR), 및 액상화 안전율(FS =CRR/CSR)을 산정하여 해석기법별 차이를 비교·분석하였다. SHAKE2000은 등가선형 해석으로 가장 보수적인 결과를, DEEPSOIL은 비선형 이력모델을 통해 비보수적인 경향을 보였다. 반면 PLAXIS 2D는 비배수 거동과 구속압 변화를 직접 고려하여 가장 현실적인 액상화 거동을 재현하였다. 또한 SPT 및 Vs 기반 CRR 산정 결과를 비교한 결과, Vs 기반 평가는 실제피해구간과의 부합도가 높아 복합 사질토 지반의 액상화 평가에 더 적합한 것으로 판단된다.
1g 진동대를 활용한 지진 발생 시 성토 사면의 붕괴 특성 평가
정수근(정회원, 조선대학교 박사과정 Member, Chosun Univ.)
김호연(정회원, (주)명동엔지니어링 과장)
김대현(정회원, 조선대학교 토목공학과 교수, dkimgeo@chosun.ac.kr)
사면 지반의 내진설계는 대부분의 실무자들이 유사 정적 해석과 같은 단순화한 방법으로 설계를 진행해왔다. 하지만 이러한 단순화된 방법은 실제 현장 조건을 완벽히 재현하는데 많은 한계가 존재한다. 이러한 한계들을 지진 강도 지표(Seismicintensity measure)를 통해 지반운동의 세기를 수치화해 손상 가능성에 대하여 설명하고 예측하기 위한 지표들을 꾸준히 연구해 왔다. 이러한 지표는 지진 발생 시 지반운동의 에너지, 지속시간과 같은 성분들을 정량적으로 표시할 수 있다. 하지만 이러한 수치들도 실제 현장에서의 관측의 어려움과 유사 정적과 같은 해석의 해석 방법으로는 실제 붕괴 시 발생하는 지진에너지에 대해 정밀하게 나타내는 데에는 많은 한계가 있다. 본 연구에서는 1g 진동대에서 조성한 1:1 모형 성토사면을대상으로, 입력 지진동 조건 변화에 따른 사면의 균열 및 붕괴 시 지진 강도 지표의 관계를 분석하였다. 입력 지진동은 10Hz0.2g, 0.28g, 0.3g 및 20Hz 0.4g의 정현파로 구성하였으며, 계측 가속도를 이용해 Arias intensity(ARI), Cumulative absolute(CAV), Vibration dose value(VDV), Root mean square acceleration(Arms)를 산정하여 시간 이력으로 비교하였다.실험 결과, 10Hz 0.2와 0.28g에서는 사면 표면에 미세한 균열만 발생하여 가속도 및 지진 강도 지표의 변화가 제한적으로 나타났다. 반면 10Hz 0.3g와 20Hz 0.4g에서는 사면에 뚜렷한 붕괴가 발생하였고, 이 시점에서 가속도 진폭이 급격히 증가하였다. 특히 ARI와 VDV는 균열과 붕괴 발생 시점에 민감하게 반응하여 CAV와 Arms에 비해 사면의 손상 정도를 더 명확히 반영하는 것으로 확인되었다. 이러한 결과는 성토사면의 실험적 붕괴 특성 평가 및 지진 재해 위험성 검토 시 ARI와 VDV를 우선적인 지진 강도 지표로 활용할 수 있음을 시사하는 것으로 판단된다
벽체 하부 공동 검측을 위한 음파 탐사시 타격 시스템의 영향
박정언(정회원, 고려대학교 건축사회환경공학과 석사과정)
이종섭(정회원, 고려대학교 건축사회환경공학부 교수)
호앙녹퀴(비회원, 캐나다 워털루 대학교 박사후 연구원)
강성훈(정회원, 고려대학교 초융합건설포렌식연구센터 연구교수, gshnice@korea.aca.kr)
벽체 구조물 배면의 공동 깊이는 공동의 위험도와 직결되므로, 공동 깊이에 따른 공동 검측 가능성에 대한 연구가 필수적이다. 본 연구에서는 공동 중심과 타격 지점 간의 거리, 해머 팁 재질, 벽체 두께와 같은 타격 시스템 변수들이 공동 검측 가능성에 미치는 영향을 평가하고자 실내 실험을 수행하였다. 모형 공동과 벽체를 포함한 토조를 조성하였으며, 상부 판으로부터의 거리를 조절하며 토조 내에 모형 공동을 매설함으로써 서로 다른 깊이의 공동을 모사하였다. 상부 판의 두께 및 해머 팁 재질을 변화시켜 음파 신호를 측정하였다. 본 연구에서는 구조물에 단위 하중이 가해졌을 때 발생하는 처짐과 동일한 개념인 유연성 값을 측정된 음파 및 하중 신호를 활용하여 산정하였으며, 이를 바탕으로 타격 시스템 변수에 따른 유연성 변화를 비교분석하였다. 실험 결과 타격 지점이 공동 중심에 근접할수록 유연성이 크게 나타났으며, 고무 팁이 플라스틱 팁에 비해 더 깊은 가탐 깊이를 보였다. 본 연구는 마이크로폰이 벽체 배면의 깊은 공동을 검측하기 위해 유용하게 이용될 수 있음을 보여준다.
불균형 다변량 데이터를 활용한 인공지능 기반 지반함몰 예측 성능 분석 및 변수 중요도 해석
김유진(정회원, 인하대학교 스마트시티공학과 석사과정)
이효범(정회원, 한국철도기술연구원 철도교통AX본부 선임연구원)
이성진(정회원, 한국철도기술연구원 궤도토목본부 책임연구원)
나선홍(정회원, 인하대학교 사회인프라공학과 부교수, s.na@inha.ac.kr)
본 연구에서는 공공데이터를 활용하여 지반함몰 발생 가능성 분석하고, 인공지능 기반 예측 모델의 적용성을 평가하였다. 연구 대상 지역으로 광주광역시를 선정하고, 최근 5년간(2019-2023) 보고된 지반함몰 사례를 기반으로 강수량, 노후건물수, 지질정보 등의 변수를 수집하여 공간 데이터셋을 구축하였다. 지반함몰 발생 비율이 극히 낮은 불균형한 데이터 특성을 고려하여 언더샘플링(Undersampling), SMOTE, 클래스 가중치(Class weight), Focal loss 등의 다양한 불균형 처리 기법을 적용하였으며, DNN, Random Forest, XGBoost 모델을 이용해 예측 성능을 비교·분석하였다. 분석 결과, 전체적인 F1-score는 낮게 나타났으나, 정밀도-재현율(Precision-Recall) 곡선을 통해 분류 성능이 유의미한 수준임을 확인하였으며, 트리 기반의 XGBoost 모델이 가장 안정적이고 우수한 성능을 보였다. 변수 중요도 분석에서는 누적 강수량(7일, 30일)과 노후건물수가 주요 영향인자로 도출되었다. 이는 지반함몰이 단기적 요인보다는 장기적인 누적 강우와 노후화된 인공 구조물의 복합적 상호작용에 의해 발생함을 시사한다.
입력 물성 변동이 균열밀도 예측에 미치는 영향: 물리 기반 탄력도와 기계학습 중요도 비교
윤형구(정회원, 대전대학교 재난안전공학과 교수, hyungkoo@dju.ac.kr)
균열밀도는 암반 및 지반 재료의 동적·탄성적 거동을 평가하는 핵심 지표로, 압축파 속도(Vp), 전단파 속도(Vs) 그리고 간극률(φ)과 밀접하게 연관된다. 본 연구에서는 풍화 실험 데이터를 기반으로 입력 물성에 1%, 2%, 5% 수준의 불확실성을 부여하여 Monte Carlo 기반 증폭 데이터를 구축하고, 균열밀도 산정식의 구조적 민감도와 데이터 기반 민감도를 종합적으로 분석하여 입력 인자의 영향성을 고찰하는 것이다. 우선, 물리식 기반 탄력도를 통해 ε이 입력 변수에 대해 갖는 국소 민감도를 정량화한 결과, 균열밀도는 전역적으로 Vp에 가장 강하게 반응하며, Vs는 특정 조건에서 매우 높은 국소 민감도를 보이는 반면 φ는 기여도가 제한적이었다. 이어서 AI 기반 변수 중요도 분석을 수행한 결과, 세 알고리즘 모두 Vp와 Vs를 균열밀도예측의 주요 변수로 식별하여 물리 기반 분석과 일관된 결론을 제시하였다. AI 분석에서는 σ 증가에 따라 Vs의 중요도가 상대적으로 크게 증가하는 경향이 관찰되었으며, 이는 탄력도 분석에서 확인된 Vs의 비선형 민감도 확장과 정확히 대응하였다. 본 연구는 물리 모델의 구조적 특성과 데이터 기반 경험적 민감도가 상호 보완적으로 해석될 수 있음을 보여주었으며, 균열밀도 예측 모델의 신뢰성 평가 및 입력 물성 관리에 기여할 수 있다.
CubeSat 위성 영상 활용한 Digital Elevation Model(DEM) 생성
박상현(비회원, 경희대학교 사회기반시스템공학과 석사과정)
신준우(정회원, 금오공과대학교 토목공학과 박사과정)
박경원(비회원, 경희대학교 사회기반시스템공학과 박사과정)
남부현(정회원, 경희대학교 사회기반시스템공학과 교수, boohyun.nam@khu.ac.kr)
고해상도 수치표고모델(Digital Elevation Model, DEM)은 재난 대응 및 지형 변화 탐지에 필수적이나, 기존 항공 LiDAR나 상용 위성은 높은 비용과 시간 제약으로 신속한 데이터 확보에 한계가 있다. 본 연구는 이러한 한계를 극복하고자, 저비용·고빈도로 전 지구를 촬영하는 초소형 위성(CubeSat) PlanetScope의 단일 스테레오 영상을 활용하여 고해상도 DEM을 생성 및 평가하는 것을 목적으로 한다. 이를 위해 설악산 국립공원을 대상으로, 적합한 스테레오 영상 쌍에 사진측량(Photogrammetry) 기법을 적용하여 4m DEM을 생성하였다. 생성된 DEM을 기존 저해상도 DEM(SRTM 30m,NGII 90m) 및 원본 영상과 비교한 결과, 본 연구에서 생성된 DEM이 저해상도 DEM에서 생략된 계곡과 능선을 명확히 묘사함을 확인하였다. 본 연구 결과는 CubeSat 단일 스테레오 영상만으로도 복잡한 산악 지형의 3D 정보 생성이 가능함을입증하였으며, 향후 CubeSat을 통한 신속하고 경제적인 지형 데이터 갱신 및 산사태·홍수 등 재난 지역 모니터링에 효과적으로 활용될 수 있을 것이다.
노유진(비회원, 충남대학교 토목공학과 석·박사통합과정)
엄세나(비회원, 충남대학교 토목공학과 학·석사연계과정)
박종전(정회원, 일신지질 서울지사 지사장)
김정환(정회원, 서울연구원 인프라기술연구실 연구위원)
이재환(정회원, 서울연구원 인프라기술연구실 연구위원)
고준영(정회원, 충남대학교 토목공학과 부교수, jyko@cnu.ac.kr)
본 연구에서는 수직증축 리모델링 시 상부하중 모델링 형태와 기초판의 강성 및 연성이 말뚝지지 전면기초 거동에 미치는 영향을 분석하고자 PLAXIS 3D를 이용한 유한요소해석을 수행하였다. 지반은 풍화토과 풍화암으로 구성하였고, 기초는 18m×18m×1m 기초판과 기존말뚝(PC 말뚝) 81본, 보강말뚝 64본(마이크로파일)로 구성하였다. 상부하중은 전체등분포하중(FDL), 기둥하중(CL), 벽체하중(WL), 부분 등분포하중(PDL;C100/C70/C50)으로 고려하고, 수직증축 시공단계에 따라 해석을 수행하였다. 해석 결과, 강성 기초판에서는 하중 모델링 방식에 관계없이 침하량은 균등하고, 축력의 경우 전체 등분포 하중 대비 기존말뚝 2%, 보강말뚝은 18% 이내로 축력 차이가 발생하였다. 연성 기초판에서는 부분 등분포하중조건에서 코어부 집중하중의 영향으로 부등침하 및 중앙부 말뚝의 축력이 크게 나타났다. 따라서, 수직증축 리모델링을 위한 보강 기초 설계 시 상부하중 모델링 형태와 기초판 특성을 함께 고려해야할 것으로 사료된다
황태훈(정회원, 서울대학교 건설환경공학부 박사과정)
응위엔부치앙(정회원, 서울대학교 BK21 인프라스피어 교육연구단 박사후연구원)
김대영(정회원, 서울대학교 건설환경공학부 석사과정)
김성렬(정회원, 서울대학교 건설환경공학부 교수, sungryul@snu.ac.kr)
지표면에 위치한 비액상화층은 지진 시 액상화를 하부의 느슨한 모래층으로 국한하여 피해를 저감한다는 현장 관측이 반복적으로 보고되었다. 또한, 이러한 다층지반 조건에서 얕은기초 건축물의 지반-구조물 상호작용은 더욱 복잡하게 나타난다. 본 연구는 1-g 진동대 모형실험을 통해 표층 비액상화층이 얕은기초 건축물의 액상화 유발 침하에 미치는 영향을 평가하였다. 얕은기초 3층 구조물을 대상으로, 표층 비액상화층이 없는 경우와 90 mm 두께의 비액상화층이 존재하는 두 조건에 대해 동일한 정현파를 적용하였다. 자유장 및 얕은기초 하부에서 과잉간극수압과 침하를 계측하고, 침하를 (1) 진동 중, (2) 액상화층 소산, (3) 표층 비액상화층 소산의 세 단계로 구분하여 해석하였다. 실험 결과, 표층 비액상화층은 자유장침하를 63%, 얕은기초 침하를 40% 감소시켰다. 또한, 표층 비액상화층이 존재하는 조건에서는 진동 후 표층 비액상화층의 소산에 의한 추가 침하가 발생함에 따라, 자유장의 주된 침하 시점이 1단계(진동 중)에서 2, 3단계(진동 후)로 전이되었다. 반면, 얕은기초 침하는 지반-구조물 상호작용에 의한 전단 유발 침하가 주된 메커니즘으로 작용하여, 표층 비액상화층의 존재여부와 무관하게 대부분의 침하는 1단계(진동 중)에서 발생하였다.
백성하(정회원, 한경국립대학교 건설환경공학부 조교수)
조진우(정회원, 한국건설기술연구원 지반연구본부 연구위원, jinucho@kict.re.kr)
본 연구에서는 현장시험을 통해 대표적인 지능형 다짐값(CMV)과 일점품질시험(들밀도시험, 평판재하시험, LWD 시험, DCP시험) 간의 상관성을 체계적으로 평가했다. CMV 및 다수 지점에서 수행된 LWD와 DCP 시험 결과는 반복 다짐에 따른 평균적 다짐품질 향상을 명확히 반영했으며, 변동계수가 약 20∼40% 범위로 나타나 성토재료 및 함수비 불균질성에 기인한 공간적 변동성이 매우 컸다. 반면, 각 단계에서 두 지점만 측정된 건조단위중량과 지지력계수는 다짐횟수 증가에 따른 뚜렷한 증가경향을 보이지 않아, 제한된 일점품질시험만으로는 넓은 시공면의 다짐 상태를 대표하기 어렵다는 점이 드러났다. 단일점 기반 분석, 전체 평균 분석, 영역 기반 분석을 비교한 결과, 영역 기반 분석이 가장 높은 상관성을 보였으며, 최적 ROI 반경은건조단위중량 1.5 m, 지지력계수 3.5 m, ELWD 2.5 m, DPI 2.0 m로 도출되었다. 이를 바탕으로 본 연구에서는 최적 ROI 내CMV 평균값과 강성 기반 일점품질시험 결과 간의 선형 회귀식을 도출하고, 품질 기준을 만족하는 일점품질시험 값과 대응하는 CMV를 목표 지능형 다짐값으로 설정하는 절차를 제안했다.
김인현(정회원, 인천대학교 도시환경공학부(건설환경공학전공) 박사후연구원)
이희준(정회원, 경일대학교 건축토목공학과 조교수, hjlee99@kiu.ac.kr)
분니(mud pumping)는 열차 하중에 의해 노반 내에서 발생한 과잉간극수압으로 세립분이 도상에 유입되는 현상으로, 도상오염과 자갈 도상의 침하를 유발한다. 일반적으로 분니는 투수계수가 낮고 배수가 불량한 점토질 노반에서 과잉간극수압증가로 인해 발생하는 것으로 알려져 있으나, 최근 연구에서는 세립분 함량이 낮더라도 내부적으로 불안정한 흙에서는 상부의 액상화 및 유동화로 인해 분니가 발생할 수 있음이 보고되고 있다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 국내 철도설계기준을 만족하는 노반재료를 대상으로 진동 삼축 실험을 수행하여 액상화 및 유동화 발생 여부를 평가하고, 노반의 내부불안정성과 도상자갈 사이노반의 세립분 이동 가능성을 분석하였다. 그 결과 내부적으로 불안정한 시료의 경우, 진동 삼축 실험 시 시료 상단부의 유동화와 내부 과잉간극수압 증가를 확인하였고, 도상자갈 사이 노반의 세립분 이동이 가능하기 때문에 내부불안정성에 의한 분니 발생 가능성을 확인하였다.
김대현(정회원, 조선대학교 토목공학과 교수)
정찬욱(정회원, ㈜정진이엔씨 대표이사)
박경호(정회원, 조선이공대학교 토목건설과 조교수, parkgeo@cst.ac.kr)
이 연구의 목적은 호남지역에서 발생한 대규모 산사태를 기반으로 산사태의 토질에 대한 특성을 분석하였다. 자연 사면에서 발생한 주요 산사태들은 산사태와 관련된 각 지질 유형의 토질 특성에 대한 정확한 분석을 통해 지반공학적 관점으로 분석하였다. 또한, 산사태의 주요 요인인 지반 매개변수의 특성 분석 결과를 바탕으로 산사태에 중요한 영향을 미치는 것으로 간주되는 전단강도를 쉽게 계산할 수 있는 모델을 제안하였다. 집중호우로 인해 산사태가 집중된 지역에서 지질 조건이 다른 편마암과 화강암의 토질 특성을 분석한 결과, 지질에 따라 다른 토질 특성을 보였다. 간극비와 공극률은 화강암 토질보다편마암 토질에서 더 크고, 건조단위중량은 편마암 토질층보다 화강암 토질층에서 더 큰 것으로 나타났다. 산사태가 발생한 자연 사면의 토질층에서 토질 특성, 투수계수, 전단강도 매개변수 간의 상관관계를 분석하였고, 이로부터 도출된 상관방정식을 사용하여 독립변수(기본 물리적 특성)의 변화로부터 종속변수(전단강도)의 변화를 예측하였다. 통계 기법을 사용하여 지반 매개변수와의 상관관계를 분석한 결과, 전단강도인 점착력은 세립토 함량 및 균등계수와 유의미한 상관관계가 있으며, 내부마찰각은 간극비, 균등계수, 건조단위중량과 유의미한 상관관계가 있는 것으로 나타났다. 화강암 및 편마암 토질층에 대해, 산사태 지역에서 중요하게 여겨지는 전단강도를 지반 매개변수와 유의미한 상관관계가 있는 물리적 특성 데이터만으로 쉽고 편리하게 추정할 수 있는 모델을 개발하였다(점착력 계산 모델 및 전단강도 계산 모델). 향후 호남지역에서 발생하는 산사태 데이터 및 지반정수를 추가함으로써 모델의 수정 및 보완을 통해 현재 모델의 신뢰성과 정확도를 향상시킬 것으로 기대된다.
김대현(정회원, 조선대학교 토목공학과 교수)
최현석(정회원, 전남개발공사 신성장사업처장)
박경호(정회원, 조선이공대학교 토목건설과 조교수, parkgeo@cst.ac.kr)
국내 서남해안지역은 연약지반으로 구성되어 있으며 이 지역에 대한 택지 및 산업단지 조성이 활발히 실시되었었다. 연약지반 현장에서 단지 매립은 필수적으로 압밀침하에 대한 문제가 발생하는데, 이에 따른 해결 방법으로 계측 및 분석을 수행하였다. 그러나 정확한 성과 분석은 기대에 미치지 못하였다. 이는 기존 연약지반의 압밀 특성 분석이 침하 형태에 따른 해석으로 국한되어 있어 과잉간극수압의 소산에 따른 과정이 해석 과정에 반영되어 있지 못하였기 때문이다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 현장 P-1-1구간을 지정하여 현장 계측자료를 이용한 e-log p' 법을 이용하여 압밀시험과 이론식인 쌍곡선법과 비교하여 최종성토 이전에 최종 침하량 예측하고자 하였다. e-log p' 법과 쌍곡선법 비교 분석결과, 간극수압이 소산되거나 잔류간극수압이 거의 남지 않을 때 쌍곡선법의 결과와 e-log p' 법의 결과는 유사하였다. 또한, 쌍곡선법은 최종성토 이후에나 최종 침하량 평가가 가능하나, 현장 계측자료를 이용한 e-log p' 법은 최종성토 이전 처녀압밀선의 작도가 가능하므로 최종성토 이전에 최종 침하량 평가가 가능한 것으로 기대된다.
박근보(정회원, 극지연구소 해양대기연구본부 연구원, kbpark@kopri.re.kr)
지구 평균 기온 상승은 산업화 이후 증가한 온실가스 배출과 밀접한 관련이 있으며, 특히 고위도 지역의 영구동토층 해빙은 저장된 유기탄소의 대기 방출을 통해 지구가열화를 가속할 잠재성이 크다. 이에 따라 동토-대기 경계면에서 발생하는 CO2 교환 특성을 정량적으로 규명하기 위한 정밀 현장 관측 기술의 필요성이 증대되고 있다. 본 연구에서는 이러한 과학적·정책적 요구에 대응하여 비분산적외선(NDIR) 분광 원리를 기반으로 한 정밀 CO2 측정시스템을 설계·제작하였다. 측정 시스템은 MCU 기반 제어기, 실시간 보정 알고리즘, 통신 모듈 및 GUI 기반 시각화 시스템을 통합하여 안정적으로 운용 가능하도록 구현하였다. 개발된 측정 시스템은 표준가스를 이용한 영점 및 스팬 교정 기능을 포함하며, 이동평균 및 적응형 필터 기반 신호 처리, 비정상 신호 제거 알고리즘, 실시간 데이터 로깅 기능을 적용하였다. 성능 검증은 0.600 ppm, 429.860 ppm,953.550 ppm의 CO2 표준가스를 이용해 정확도, 정밀도, 응답시간, 선형성 및 영점 안정성을 평가하는 방식으로 수행하였다. 실험 결과, 모든 농도 구간에서 측정값은 표준가스 농도와 일치하는 수준을 유지하였으며, 정확도 ±1% 이내, 정밀도 0.560이하, 장기 영점 드리프트를 포함하여 상용되고 있는 정밀 측정 시스템(LI-COR LI-7810)와 동등한 성능을 확보하였다. 또한1:1 비교 분석에서 두 장비의 측정값은 높은 상관성을 보이며 우수한 선형성을 나타냈다.
영문논문집 개요 소개
Numerical study to evaluate the effect of encased stone columns technique for liquefactionmitigation of sandy soil by PLAXIS 2D
Ahmed O. K. Mahmoud1*, Khaled Abdelsamie1, Hesham G. Nouby2 and Mohamed M. A. Hussein1
1 Civil Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering, Sohag University, Sohag 82524, Egyp
2 Civil Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering, Sphinx University, P.O. Box 10, New Assuit City, Egypt
*Correspondence: Ahmed O. K. Mahmoud ahmed.mahmoud@eng.sohag.edu.eg
Liquefaction of sandy soil under seismic loading is a serious hazard to infrastructure due to excessive grounddeformation and bearing strength loss. Various ground improvement techniques have been attempted to address theissue, of which encased stone columns (ESC) have recently shown great promise. While stone columns (SCs) providedrainage and reinforcement, adding a geosynthetic encasement contributes lateral support and potentially seismicperformance. This study employs 2D finite element modeling with PLAXIS 2D and the UBC3D-PLM model to predictthe performance of ESC in liquefaction mitigation. It is validated with laboratory experiments and simulation of threecases: without SC, with SC, and with ESC. The performance of the three is compared based on the excess pore waterpressure ratio (ru), excess pore water pressure (EPP), settlement, and effective stresses. The 1940 El Centro earthquakewas utilized as input motion to simulate dynamic conditions. Parameters such as column spacing, diameter,permeability, and encasement stiffness are considered. The results indicate that ESCs improve the soil responsesignificantly during seismic loading. ESCs decrease the EPP buildup to less than in other cases and lower groundsettlement than SC due to encasement. Reducing spacing-to-diameter (s/d) values and higher permeability enhancedrainage and induce faster pore pressure dissipation. ESCs also increase effective stress and aid in managing verticaland lateral deformations. Therefore, the results illustrate the performance of ESCs in improving ground stability andliquefaction resistance during earthquakes.
An analytical model for stability analysis of a rock slope toppling mechanism driven by externalloading
Hao Cheng1,2,3*, Yongjun Song1 and Linyuan Han1
1 School of Civil Engineering, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, Hubei, People’s Republic of China
2 Wuhan University Shenzhen Research Institute, Shenzhen 518057, Guangdong, People’s Republic of China
3 Key Laboratory of Disaster Prevention and Control for Noncoal Open-pit Mines, National Mine Safety Administration, Maanshan 243071, Anhui,People’s Republic of China
*Correspondence: Hao Cheng chenghaomail@whu.edu.cn
The flexural toppling failure of anti-dip rock slopes (ADRSs) may happen under the action of external loads. Evaluatingthe stability of ADRSs subjected to external loads can guide slope protection and engineering construction. In thispaper, the failure modes and failure surface of ADRSs are determined based on the experiments and numericalsimulations. In the framework of the limit equilibrium method and cantilever beam model, an analytical model forassessing the stability of ADRSs is proposed. Then, the effects of the loading length, thickness of rock layer, strength parameters of persistent discontinuity and critical tensile strength of intact rock layer on the stability of ADRSs arediscussed. It is found that the thickness of rock layer, cohesion and friction angle of the persistent discontinuity andcritical tensile strength of intact rock layer significantly enhance the stability of ADRSs, while the external loads andloading length acting on the top edge are harmful to the stability of ADRSs. In addition, the correctness and practicalityof the proposed method are verified by two typical cases. Factor of safety from the proposed method are consistentwith those from the previous studies.
Marble processing waste as a sustainable structural fill materail in reinforced soil structures
Jagdish Lohara1 and Neha Shrivastava1 *
1 Department of Civil Engineering, Malaviya National Institute of Technology, Jaipur, Rajasthan 302017, India
*Correspondence: Neha Shrivastava neha.ce@mnit.ac.in
Efforts to recycle marble processing waste (MPW), a by-product of dimensional marble production, are essential inmitigating environmental impacts but face challenges such as composition variability, low inclusion rates, andpreprocessing requirements in current practices. This study evaluates the feasibility of utilising MPW as a sustainablestructural fill material in Reinforced Soil Structures (RSS), an inevitable part of transportation infrastructure.Comprehensive characterisation of MPW--including particle gradation, plasticity, hydraulic conductivity,electrochemical properties, morphology, mineralogical composition, and shear strength--demonstrates its suitability asa structural fill material, comparable to Local Soil(LS). Although MPW exhibits slightly lower interaction characteristicswith geogrids compared to LS, as evidenced by interaction coefficients (Ri) and interface apparent coefficients(μs/GSY) obtained from interface shear and pullout tests, the differences are minimal. For the MPW-geogrid interface,Ri and μs/GSY values ranged between 0.70-0.85 and 0.25-1.38, respectively. Being non-hazardous andenvironmentally safe, along with offering environmental benefits and approximately 51% cost savings in fill material,MPW establishes itself as a viable and sustainable alternativet o natural soil. This addresses the dual challenges of MPWdisposal while meeting the growing demand for structural fill,c ontributing to natural soil conservation efforts.
Investigation into the effect of the grout properties injected behind the segment on surfacesettlement in mechanized tunneling
Haniyeh Kouhia1, Hamid Chakeri1*, Mohammad Darbor1, Hamed Baghali1 and Hamid Mousapour1
1 Department of Mining Engineering, Sahand University of Technology, Tabriz, Iran
*Correspondence: Hamid Chakeri chakeri@sut.ac.ir
Ground surface settlement is one of the inevitable components of shallow excavations in soil environments. It is crucialto predict the amount of ground surface settlement in mechanized tunneling for urban subway construction. Some ofthe factors affecting ground surface settlement are geotechnical properties of the environment, the face pressure,overburden pressure, and proper injection pressure. In this study, the influence of grout injection on surface settlementin mechanized tunneling was investigated using both physical modeling and numerical simulations. Key parametersexamined include grout injection pressure (0.5 to 4 bar), dry soil density (1,600 and 1,700 kg/m³), and the geometryof the gap behind the tunnel segment (symmetric and asymmetric). A custom experimental setup was developed tosimulate tunnel conditions and measure resulting settlements under controlled conditions. The results indicated thatwith an increase in injection pressure and soil density, the amount of settlement decreased. For instance, in soilcompaction with 2 blows and an equivalent pressure of 1.5 bar, the settlement decreased by 33% compared to anequivalent pressure of 0.5 bars. Moreover, in soil compaction with 5 blows and an equivalent pressure of 1.5 bar, theground settlement decreased by approximately 50% compared to soil compaction with 2 blows. Additionally, theinvestigation of the effect of the void space behind the segment (gap) showed that asymmetric voids lead to increasedsettlement compared to symmetric voids.
Energy-efficient artificial freezing of multilayer soil systems: case studies of three different mineshafts under construction
Mikhail Semin1*, Alyona Dunkina1 and Sergey Bublik1
1 Mining Institute of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Perm, Russia
*Correspondence: Mikhail Semin seminma@inbox.ru
Artificial ground freezing (AGF) is widely applied to ensure the safe sinking of vertical mine shafts through flooded andunstable soils. In multilayer soil systems, the thermophysical and mechanical properties of individual layers differsubstantially, resulting in variations in the required frozen-wall (FW) thickness and the time needed to achieve it. Thisleads to an imbalance in the freezing process, where some layers become over-frozen while others remain underfrozen,causing excessive energy consumption and potential safety risks. Improving the energy efficiency of AGF undersuch conditions requires a better understanding of freezing unevenness in practical engineering cases. This studyanalyses three AGF projects for potash mine shafts with freezing depths ranging from 185 to 530 m and differinghydrogeological conditions. The research combines detailed design documentation, field monitoring data, andvalidated heat transfer modelling to examine vertical unevenness in soil freezing across multilayer systems. Based onthis analysis, new quantitative criteria are proposed for assessing freezing unevenness. Using these criteria, severalenergyefficiency enhancement measures are developed, including interval-based excavation permissions, adjustmentof excavation technological parameters, step freezing, and zonal thermal insulation. A comparative evaluation of thefreezing system at each site demonstrates that the proposed measures can significantly reduce energy consumption,with potential savings varying across sites depending on geological conditions. The results provide a practicalframework for diagnosing and mitigating freezing unevenness in multilayer soils, supporting both safer constructionand more energy-efficient AGF operations in deep mine shaft sinking.
Applicability of 3D laser scanning and close-range photogrammetry for geotechnical laboratorytests
Ali M. Basha1, Hany El Naggar2, Mohamed M. Sherif1 and Mohamed H. Zakaria1*
1 Civil Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering, Kafr El Sheikh University, Kafr E-lSheikh City 33511, Egypt
2 Department of Civil and Resource Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Dalhousie University, Halifax B3H 4R2, Canada
*Correspondence: mohammed_hamed@eng.kfs.edu.eg
Non-contact surveying strategies such as terrestrial laser scanning (TLS) and digital close-range photogrammetry(DCRP), have recently become popular as surveying techniques due to their rapid deployment and high accuracy. Thecritical issue that researchers typically face is the limited number of LVDTs or dial gauges available in laboratories, andoccasionally it might be physically challenging to install several gauges in the testing facilities. Consequently, the primaryobjective of this paper is to examine the present viability and benefits of employing TLS and DCRP techniques inmonitoring geotechnical applications. Calibration of these methods was performed through two laboratory tests: (1)monitoring of secant pile walls (SPW) as well as the soil movements; and (2) axial compression tests on SPW. Thefindings reveal that the discrepancy between traditional measurement methods and the TLS approach is less than3.0%, whereas the difference between traditional methods and DCRP is under 1.8%. Furthermore, both DCRP andTLS techniques are capable of precisely tracking initial deformations, geometric irregularities, deficiencies in thesamples(including pre-buckling phenomena), and deformations of the soil tank at each stage of loading. In conclusion,TLS and DCRP methods were found to offer accurate and advantageous alternatives for geotechnical monitoring,notably their capacity for the automatic collection and analyssi of an unlimited number of measurement points.
A refined method for determining equivalent radius (Req) in resonant column tests across a widestrain range
Tien Hue Nguyen1, Taebong Ahn2 and Yujin Lim1*
1 Department of Civil and Railroad Engineering, Paichai University, Daejeon 35345, Korea
2 Department of Civil and Railway Systems, Woosong University, Daejeon 34606, Korea
*Correspondence: Yujin Lim yujin@pcu.ac.krThe equivalent radius Req has been used for calculation of strain in Resonant Column (RC) testing. Present calculation methods for Req are not adequate since they are not precise over a wide range of strain. In this study, a new equation of Req that can be used over a wide range of strain is proposed by developing a new method of determining Req basedon a numerical integration technique using a theoretical modified hyperbolic model. The new method for obtaining optimum Req can be used for evaluating shear modulus more precisely in an RC test at any strain level. The prediction equation of Req was successfully applied to typical unbound granular materials such as the simulated lunar granularsoils to get the shear modulus reduction curves. The Req values computed using the developed equation slope down sharply when the strain value varies from 0.1 to 0.001. The conventional equivalent radius approach could be inadequate at small strains less than 0.01. This means that for obtaining the best results from the RC testing, differentvalues of Req must be used considering the range of shear strain.
회원동정
2025년 12월 신규가입자
12966, 고창훈, 정회원, 한국토지주택공사 경기남부지역본부 차장
12967, 원철연, 종신회원, 한국토지주택공사 충북지역본부 건설관리관
12968, 김경준, 정회원, 세현지오텍 기술사사무소 소장
12969, 문준성, 정회원, 부산대학교 사회환경시스템공학과 대학원생
12970, 박남진, 종신회원, 한국토지주택공사 스마트도시계획처 차장
12971, 박주영, 종신회원, 도건이엔씨 대표
12972, 방승아, 정회원, ㈜피아이컴퍼니 기업부설연구소 기술전략팀 선임
12973, 신상협, 종신회원, 한화 인프라VE팀 과장
12974, 신정훈, 정회원, 지음컨설턴트 대표
12975, 안중빈, 종신회원, 한국토지주택공사 화성사업본부 단지조성2팀 대리
12976, 원조현, 종신회원, 부산대학교 사회환경시스템공학과 박사과정
12977, 차재호, 정회원, 국립부경대학교 토목공학과 대학원생
12978, 최진호, 종신회원, 광주광역시 서구 시설관리공단 본부장
12979, 황덕휘, 종신회원, 한국과학기술원 건설환경공학과 박사과정
총 14명 (정회원 6명/종신회원 8명)
학생회원
111255, 김영국, 학생회원, 국립부경대학교 토목공학과 학부생
111256, 백민준, 학생회원, 단국대학교 토목환경공학과 학부생
승급회원(학생회원 → 정회원)
12980, 이유성, 정회원, 가천대학교 토목환경공학과 대학원생

여러분, 안녕하십니까. 이번호 편집을 담당한 안재광입니다.
원고를 작성하는 지금은 한 해의 끝을 정리하는 시간입니다. 새해의 시작을 알리는 2026년 1호를 편집하는 동안 저는 땅과 우리의 시간을 원고 사이사이에서 여러 번 만났습니다. 한 편의 글이 지면으로 옮겨지기까지, 문장의 온도와 그림의 선명함, 숫자와 용어의 정확함을 함께 지켜주신 집필진과 편집위원 여러분께 먼저 깊이 감사드립니다.
이번 호의 회장님의 신년 인사와 함께 시작에 어울리는 ‘미래 혁신’ 이라는 울림으로 포문을 열었습니다. 권두언은 학회의 미래를 “우물”에 비유하며, 결국 혁신이란 갑자기 솟아나는 기적이 아니라, 사람과조직, 지역과 세대가 차곡차곡 쌓아 올린 깊이에서 길어 올려지는 것임을 조용히 일깨워 주었습니다. 특히 YGE와 지역위원회를 축으로 한 연결의 이야기는, ‘학회’가 사람과 사람 사이의 연결다리라는 점을 다시 생각하게 하였습니다.
특별테마에서 선보인 하이퍼루프는 우리가 그리는 새로운 미래를 엿볼 수 있었습니다. “빈 공간을 유지하는 기술”이 도시의 혼잡과 환경 부담을 바꿀 수 있다는 상상은, 지반공학이 다루는 ‘보이지 않는 영역’이 얼마나 넓어졌는지 보여준 것 같습니다. 기술기사에서는 매립지 연약지반에서의 연동침하라는 현실적인 문제 앞에서, 시공성과 효과를 함께 잡기 위한 고민이 선명하게 드러납니다. 사석·암반층 조건에서의시트파일 시공 사례는 “원리”가 “현장”에 닿을 때 생기는 마찰과 타협, 그리고 그 사이에서 탄생하는 실용적 해법을 담고 있습니다.
‘흙, 돌 그리고 나’의 두 글은 서로 다른 결로 마음을 흔듭니다. 산사태 답사기는 짧고 굵게 쏟아진 비가남긴 상처를, 현장의 냄새와 경사, 발걸음의 무게로 전합니다. 보고서의 문장으로는 다 담기 어려운 긴장감 “현장을 본 사람만이 아는 감각” 이 글의 가장 큰 힘이었습니다. 한편, 아시안 평생공로상 수상 소감은한 연구자의 시간이 곧 한 학문의 역사로 이어질 수 있음을 보여줍니다. 수십 년 동안 흙을 만지고, 학생을길러내고, 국제 무대에서 한국 지반공학의 이름을 쌓아 올린 여정은, 읽는 내내 ‘경력’이 아니라 헌신이라는 단어로 다가왔습니다.
‘젊은 지반공학자’ 코너는 또 다른 의미에서 반가웠습니다. 연구실에서 시작된 질문이 현장과 제도로이어지고, 다시 새로운 연구의 씨앗이 되는 흐름. 요즘 공학이 요구하는 속도는 빠르지만, 결국 길게 남는것은 “현장에 닿는 지식”이라는 사실을 담담하게 보여주었습니다.
올해는 Q&A를 처음 선보였습니다. 그 시작을 많은 사람들이 편하게 이용하는 서울 지하철로 하였습니다. 서울시 지하안전 제도와 운영 시스템을 통해 ‘지하’가 더 이상 막연한 공간이 아니라, 법·기술·운영이 맞물려 관리되어야 할 도시의 기반임을 확인할 수 있었습니다. 앞으로 이 코너가 실용적이고 학문적으로 이어지길 기대합니다. 학생기자단의 GER 국제학술대회 후기는, “학회”가 발표만 하는 자리가 아니라사람을 만나고, 질문을 주고받고, 미래의 협력을 준비하는 자리라는 것을 다시 보여줍니다. 짧은 발표와긴 대화가 중심이 되는 토론 형식, 서로 다른 나라의 연구자들이 가까운 거리에서 나누는 문제의식의 공유는 너무나 중요한 것 같습니다.
마지막으로 여행스케치는 본인이 새로운 정착지에서 느낀 감정 스케치로 그려보았습니다. 삼척의 일출, 케이블카 아래로 펼쳐지는 바다, 도계의 겨울의 순간들을 회원들과 공유하고 싶었습니다. 원고를 마감하며, 본인이 느낀 학회지는 결국, 새로운 정보도 주고, 우리 회원이 한 해 동안 무엇을 중요하게 여겼는지의 기록으로 보여졌습니다. 이 한 권이 회원 여러분의 책상 위에서 잠깐이라도 손을 멈추게 하고, 생각을 이어주고, 마음을 따뜻하게 해주길 바랍니다.
회원 여러분의 한 해가, 안전하고 평안하기를 기원합니다.
안재광
편집위원회 부위원장
강원대학교 교수



















































